RICKETS:
Q&A COUNT: 16*
Clinical Features of Rickets
Reason for Recurrent Respiratory Tract infection in Rickets
HYPOTONIA
EXAMINATION:
Fontanelles, Bossing, Craniotabes:
Method of measuring Anterior Fontanelle
CRANIAL BOSSING?
Characterized by rounded prominence at centre of skull bones
Causes of bossing at different skull bones:
Frontal & parietal bossing - Rickets
Occipital bossing - Thalassemia
What is Craniotabes?
Thin, parchment like soft areas that can be intended like ping pong ball, along suture lines. Seen preferably in Parietal bones.
Causes:
1. Physiological - upto 3 months
2. Rickets
3. Hydrocephalus, Hypervitaminosis A, Osteogenesis imperfecta, Congenital syphilis
Difference between Rickety Rosary and Scorbutic Rosary
Rickety Rosary is due to Vitamin D deficiency
Scorbutic Rosary is due to Vitamin C deficiency.
Scorbutic Rosary characteristically causes painful angular swellings or beadings in the costo-chondral junction - the child feels painful even to do normal breathing**
In Rickets - the costo-chondral junction is dome dome shaped and semi circular. It will be painless
INVESTIGATIONS:
Radiological features of Rickets (there are totally 20 findings)
X Ray WRIST is the most important X ray in a case of Rickets as it reveals many findings!
X ray WRIST - Findings:
Epiphysis:
1. Delayed appearance of epiphysis
2. Widended epiphysis
3. Cupping of the margins at the end of the bones
4. Height of epiphyseal plate is increased
5. Splaying
6. Fraying at the margins at the end of the bones due to lateral bulging of osteoid tissue
Metaphysis:
1. Cupping and Widening
2. Trumpeting
3. Exaggerated normal concavity
4. Irregular calcification
Diaphysis:
1. Thinned out cortex
2. Bending of long bones
3. Decreased density
4. Coarse and prominent trabecula
5. Double contour appearance of shaft of radius
6. Fractures and deformities
7. Appearance of Seperation of diaphysis from periosteum (due to uncalcified osteoid)
8. Distance between provisional zone of calcification and epiphysis is more than normal for particular age
Other X Ray Findings:
1. X ray Skull - Widening of sutures
2. Cupping and Widening of lower end of Tibia and Fibula
X Ray findings in Scurvy:
1. Ground glass appearance of long bones
2. Pencil thin cortex
3. White line of Frankel - irregular, thickened line in metaphysis*. It represents zone of well calcified cartilage
4. Trummerfeld zone - zone of rarefaction in Metaphysis (poor trabuculae formation), found proximal to white line of Frankel
5. Pelken spurs - Lateral part of Trummerfeld zone appears as a triangular defect (seen in Metaphysis)
6. Wimberger ring sign - Thin white line in Epiphysis*
TREATMENT for Rickets:
Vitamin D
1500-5000 IU/day orally for 6-10 weeks
(or)
STROSS REGIME: Alternate single day dose 600000 IU Intramuscular
(Or)
15000 microgram of Vitamin D3 (orally in 4-6 divided doses)
Within 2-4 weeks, X ray demonstrates evidence of healing*
Now, give daily intake Vitamin D 400 IU/day for 2-3 months
Types of Rickets:
1. Nutritional Rickets - Vitamin D low intake
2. Vitamin D Dependent Rickets Type 1 (VDDR Type 1) - 1 alpha hydroxylase deficiency in kidneys
3. VDDR type 2 - Cellular Resistance to Vitamin D. Responds only to high doses due to partly functional receptors
4. Vitamin D resistant rickets - characterized by hypophosphatemia (occurs familial or oncogenic) (Mechanism: More FGF-23 stimulates more phosphatase - resulting in low phosphate)
5. Renal Osteodystrophy - give phosphate binder to prevent hyperphosphatemia*
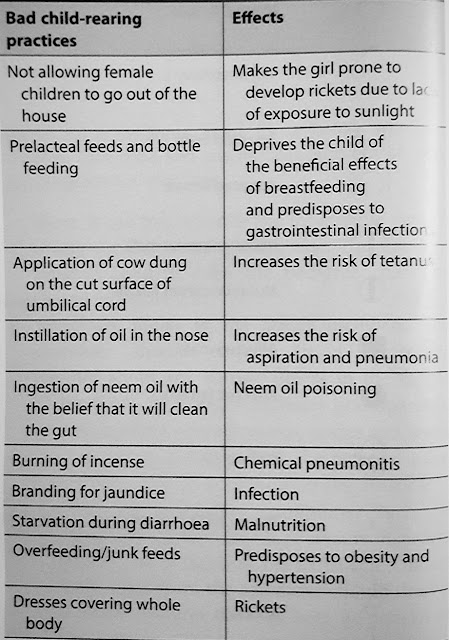
Prevention of Rickets
400 IU of vitamin D3 should be given to all children till 1 year of age
Q&A COUNT: 16*
Clinical Features of Rickets
 |
| This picture is taken from Aruchamy textbook of Paediatrics |
Reason for Recurrent Respiratory Tract infection in Rickets
HYPOTONIA
What is recurrent Respiratory Tract infection? (or) Tell criteria to say it is recurrent RTI
6-8 episodes of Respiratory Infection in every year
EXAMINATION:
Fontanelles, Bossing, Craniotabes:
Fontanelles - age of closure?
AF by 7-19 months
PF by 2 months
Since delayed closure of AF is seen in Rickets, normal closure age can be asked
Since delayed closure of AF is seen in Rickets, normal closure age can be asked
Method of measuring Anterior Fontanelle
Normally it would be around 2 x 2 cm approximately
Significance of Bulging of Anterior Fontanelle other than Rickets
Significance of Bulging of Anterior Fontanelle other than Rickets
It is a Clinical sign for Increased Intracranial pressure which occurs in children
This is considered to be a contra-indication for Lumbar puncture*
CRANIAL BOSSING?
Characterized by rounded prominence at centre of skull bones
Causes of bossing at different skull bones:
Frontal & parietal bossing - Rickets
Occipital bossing - Thalassemia
What is Craniotabes?
Thin, parchment like soft areas that can be intended like ping pong ball, along suture lines. Seen preferably in Parietal bones.
Causes:
1. Physiological - upto 3 months
2. Rickets
3. Hydrocephalus, Hypervitaminosis A, Osteogenesis imperfecta, Congenital syphilis
Difference between Rickety Rosary and Scorbutic Rosary
Rickety Rosary is due to Vitamin D deficiency
Scorbutic Rosary is due to Vitamin C deficiency.
Scorbutic Rosary characteristically causes painful angular swellings or beadings in the costo-chondral junction - the child feels painful even to do normal breathing**
In Rickets - the costo-chondral junction is dome dome shaped and semi circular. It will be painless
INVESTIGATIONS:
Radiological features of Rickets (there are totally 20 findings)
X Ray WRIST is the most important X ray in a case of Rickets as it reveals many findings!
X ray WRIST - Findings:
Epiphysis:
1. Delayed appearance of epiphysis
2. Widended epiphysis
3. Cupping of the margins at the end of the bones
4. Height of epiphyseal plate is increased
5. Splaying
6. Fraying at the margins at the end of the bones due to lateral bulging of osteoid tissue
Metaphysis:
1. Cupping and Widening
2. Trumpeting
3. Exaggerated normal concavity
4. Irregular calcification
Diaphysis:
1. Thinned out cortex
2. Bending of long bones
3. Decreased density
4. Coarse and prominent trabecula
5. Double contour appearance of shaft of radius
6. Fractures and deformities
7. Appearance of Seperation of diaphysis from periosteum (due to uncalcified osteoid)
8. Distance between provisional zone of calcification and epiphysis is more than normal for particular age
Other X Ray Findings:
1. X ray Skull - Widening of sutures
2. Cupping and Widening of lower end of Tibia and Fibula
X Ray findings in Scurvy:
1. Ground glass appearance of long bones
2. Pencil thin cortex
3. White line of Frankel - irregular, thickened line in metaphysis*. It represents zone of well calcified cartilage
4. Trummerfeld zone - zone of rarefaction in Metaphysis (poor trabuculae formation), found proximal to white line of Frankel
5. Pelken spurs - Lateral part of Trummerfeld zone appears as a triangular defect (seen in Metaphysis)
6. Wimberger ring sign - Thin white line in Epiphysis*
TREATMENT for Rickets:
Vitamin D
1500-5000 IU/day orally for 6-10 weeks
(or)
STROSS REGIME: Alternate single day dose 600000 IU Intramuscular
(Or)
15000 microgram of Vitamin D3 (orally in 4-6 divided doses)
Within 2-4 weeks, X ray demonstrates evidence of healing*
Now, give daily intake Vitamin D 400 IU/day for 2-3 months
Types of Rickets:
1. Nutritional Rickets - Vitamin D low intake
2. Vitamin D Dependent Rickets Type 1 (VDDR Type 1) - 1 alpha hydroxylase deficiency in kidneys
3. VDDR type 2 - Cellular Resistance to Vitamin D. Responds only to high doses due to partly functional receptors
4. Vitamin D resistant rickets - characterized by hypophosphatemia (occurs familial or oncogenic) (Mechanism: More FGF-23 stimulates more phosphatase - resulting in low phosphate)
5. Renal Osteodystrophy - give phosphate binder to prevent hyperphosphatemia*
Prevention of Rickets
400 IU of vitamin D3 should be given to all children till 1 year of age