BREAST FEEDING and DIET HISTORY
Q&A COUNT: 32*
Topic 2: WEANING and COMPLEMENTARY FEEDING: 06*
Difference between Weaning and Complementary feeds
Weaning - stop breastfeeding and take solid foods only (after 6 months)
Complementary feeding - continue breastfeeding after 6 months, but add solid foods in addition
Foods given for Weaning and complementary foods are same*
*******
Q&A COUNT: 32*
Topic 1: BREAST FEEDING
Q&A COUNT: 17*
When will be the first breastfeed given?
Q&A COUNT: 17*
When will be the first breastfeed given?
Within 1/2 an hour - normal delivery
Within 4 hours - Caeserean
Within 4 hours - Caeserean
What is Exclusive breastfeeding?
For first 6 months, only breastmilk should be given to the baby. No other fluids or feeds including water to be given, with an exception of drops, syrups and ORS.
This is called exclusive breastfeeding
This is called exclusive breastfeeding
Why duration of exclusive breastfeeding is fixed to be 6 months?
Reasons:
- Taste buds connect to cortex by 3-4 months which is required for Co-ordination of movements for food
- Time required to develop Head control
- Salivation (indicates enzyme release for digestion) takes time to develop
Why water is avoided in exclusive breastfeeding?
Liquids allowed for first 6 months during exclusive breastfeeding:
- Breast milk
- OPV
- Vitamin syrups
- ORS
Any myth about lactation?
- For first 3 days, milk will come like water. So do not give milk for first 3 days
What are Hunger cues? List out some Hunger cues*
Behaviour of a baby which shows that it is HUNGRY
It includes the following:
Behaviour of a baby which shows that it is HUNGRY
It includes the following:
Early Hunger Cues:
- Lips licking
- Sucking hands, lips, toes, fingers or even clothes and toys
- Opening and closing mouth
- Protrude tongue out
- Move head side to side
Hunger cues:
- Attempt to get into feeding position by pulling mother's clothes
- Increased leg and arm movements
- Fast breathing
- Showing discomfort by making whining sounds or grunts (this does not include hunger cry)
Late Hunger cues:
- Moving head from one side to other
- HUNGER CRY**
Colustrum - Volume:
Volume per day 5-10 ml (equivalent to volume of stomach is 5 ml in day 1)
Comes for first 2-3 days
Uses/Advantages of Colustrum:
1. Rich in Immunoglobulins, High immunity conferred to baby
2. Rich in nutrients
3. Anti microbial in nature
4. Mild laxative effect (helps to pass early stools)
Comes for first 2-3 days
Uses/Advantages of Colustrum:
1. Rich in Immunoglobulins, High immunity conferred to baby
2. Rich in nutrients
3. Anti microbial in nature
4. Mild laxative effect (helps to pass early stools)
How to check Adequacy of breast feeding?
1. Drinks breastmilk for 8-10 times a day, including 2 night time breastfeeds
2. Passes urine 6-8 times a day
3. Gains weight adequately
4. Demands next feed after 2-3 hours from previous breastfeeding
1. Drinks breastmilk for 8-10 times a day, including 2 night time breastfeeds
2. Passes urine 6-8 times a day
3. Gains weight adequately
4. Demands next feed after 2-3 hours from previous breastfeeding
Proper positioning for breastfeeding and Good attachment in breastfeeding
 |
| The above picture is taken from Aruchamy Textbook of Paediatrics |
10 steps of Baby Friendly Hospital Initiatives??
Mnemonic: "10 STEPS for DEAR Infants"
10 - refers to 10 steps
S- Show mother how to Breastfeed
T- Train all healthcare staffs in skills
E- Establishment of breastfeeding support groups, refer mothers to them
P- breastfeeding 'Policy' routinely recommended to all health care staff
S - Start breastfeeding within half hour of birth
D- Breastfeeding on 'Demand'
I- Inform mother about benefits/management of breast feeding
Mnemonic created by Stanley CM Medonics, India
What are the Problems associated with Breast feeding?
1. Breastfeeding Jaundice
2. Breastmilk Jaundice
3. Vitamin K deficiency
4. PEM (due to prolonged breastfeeding without complementary feeds, as demands increase after 6 months)
5. Drugs, Toxins, Infections (HIV,HBV,CMV) transfer
What is the Problem with Prolonged Exclusive breastfeeding?
Risk of PEM (due to prolonged breastfeeding without complementary feeds, as demands increase after 6 months)
List out the Contraindications of Breastfeeding!
Maternal - Maternal psychosis, drug intake (antimetabolites, antithyroid drugs, anticoagulants)
Neonatal - Inborn errors of metabolism
Note: Standard books say - breastfeeding is continued in case of breastmilk jaundice, breast abscess or cracked nipple
*******
10 - refers to 10 steps
S- Show mother how to Breastfeed
T- Train all healthcare staffs in skills
E- Establishment of breastfeeding support groups, refer mothers to them
P- breastfeeding 'Policy' routinely recommended to all health care staff
S - Start breastfeeding within half hour of birth
D- Breastfeeding on 'Demand'
E- Exclusive Breastfeeding
A - Avoid any manufactured infant formula, food or Feeding bottles
A - Avoid any manufactured infant formula, food or Feeding bottles
R- Rooming-in
Mnemonic created by Stanley CM Medonics, India
What are the Problems associated with Breast feeding?
1. Breastfeeding Jaundice
2. Breastmilk Jaundice
3. Vitamin K deficiency
4. PEM (due to prolonged breastfeeding without complementary feeds, as demands increase after 6 months)
5. Drugs, Toxins, Infections (HIV,HBV,CMV) transfer
What is Breast Milk Jaundice?
Jaundice due to Breast milk drinking (due to inhibitory factors in breast milk - PREGANANEDIOL and FREE FATTY ACIDS)
Occurs beyond 3rd to 4th week of Jaundice
Note: Breastfeeding should not be stopped for diagnosis or treatment of this Jaundice
Occurs beyond 3rd to 4th week of Jaundice
Note: Breastfeeding should not be stopped for diagnosis or treatment of this Jaundice
What is Breast feeding Jaundice?
Breast feeding Jaundice is due to inadequate breastfeeding
Occurs between 2nd and 3rd day
*Kindly understand the opposite nature of the above two Jaundice types
Occurs between 2nd and 3rd day
*Kindly understand the opposite nature of the above two Jaundice types
What is the Problem with Prolonged Exclusive breastfeeding?
Risk of PEM (due to prolonged breastfeeding without complementary feeds, as demands increase after 6 months)
List out the Contraindications of Breastfeeding!
Maternal - Maternal psychosis, drug intake (antimetabolites, antithyroid drugs, anticoagulants)
Neonatal - Inborn errors of metabolism
Note: Standard books say - breastfeeding is continued in case of breastmilk jaundice, breast abscess or cracked nipple
*******
Topic 2: WEANING and COMPLEMENTARY FEEDING: 06*
Difference between Weaning and Complementary feeds
Weaning - stop breastfeeding and take solid foods only (after 6 months)
Complementary feeding - continue breastfeeding after 6 months, but add solid foods in addition
Foods given for Weaning and complementary foods are same*
Why weaning or Complementary feeding to be done at 6 months?
- Baby demands becomes more than what is provided by breastmilk alone (due to weight gain)
- Mother secretion becomes less after 6 months
Types of Weaning/Complementary Food
- Natural Weaning Food
- IMS (Infant Milk Substitute) (learn about which year - IMS act was passed - "1972")
How weaning or adding solid foods is done step by step? (or) Comment on appropriate weaning foods
Weaning must be done as a slow process..
- First start with a monocereal at 7th month
- Then add pulses
- Then give Rice Kanji/ Ragi koozh
- Then give smashed vegetables
- Then you shall give IDLY
- Then give Banana
- Give EGG Yellow at 9 months
- Give EGG White (little late) at 1 year age (due to allergy)
Bad weaning foods:
Biscuit and Cow's milk
Disadvantage of delayed weaning:
- Malnutrition
- Iron deficiency anemia
*******
Topic 3:
PRELACTEAL AND BOTTLE FEEDS: 05*
PRELACTEAL AND BOTTLE FEEDS: 05*
What are Prelacteal feeds?
Artificial feeds or drinks which are given even before breast feeding is initiated
Usually given on day 1
It is a ritual among Hindus and Muslims.
Usually given on day 1
It is a ritual among Hindus and Muslims.
Prelacteal feeds - Complication (Infections)
1. Infection
2. Allergies
3. Interfere with suckling
4. Accepts less breastmilk, since hunger is satisfied
5. Less stimulation of breast - less establishment of breastfeeding
6. Mother likely to suffer breast conditions such as engorgement
7. Nipple confusion (due to bottle feeds)
2. Allergies
3. Interfere with suckling
4. Accepts less breastmilk, since hunger is satisfied
5. Less stimulation of breast - less establishment of breastfeeding
6. Mother likely to suffer breast conditions such as engorgement
7. Nipple confusion (due to bottle feeds)
Prelacteal feeds - Common feeds given
1. Honey
2. Jaggery
3. Ghee
4. Sugar water
5. Herbal paste
1. Honey
2. Jaggery
3. Ghee
4. Sugar water
5. Herbal paste
Bottle feeds - disadvantages
1. Infection
2. Allergies
3. Lack of all advantages obtained from breastfeeding
4. Interfere with suckling and less stimulation of breast - less establishment of breastfeeding
5. Mother likely to suffer breast conditions such as engorgement
6. Nipple confusion (due to bottle feeds)
2. Allergies
3. Lack of all advantages obtained from breastfeeding
4. Interfere with suckling and less stimulation of breast - less establishment of breastfeeding
5. Mother likely to suffer breast conditions such as engorgement
6. Nipple confusion (due to bottle feeds)
What is Bad CRP (Child Rearing Practices)? Mention them
Bad CRP are those socio-cultural practices which are harmful to baby. Bottle feeds and prelacteal feeds are examples of Bad CRP
Bad CRP are those socio-cultural practices which are harmful to baby. Bottle feeds and prelacteal feeds are examples of Bad CRP
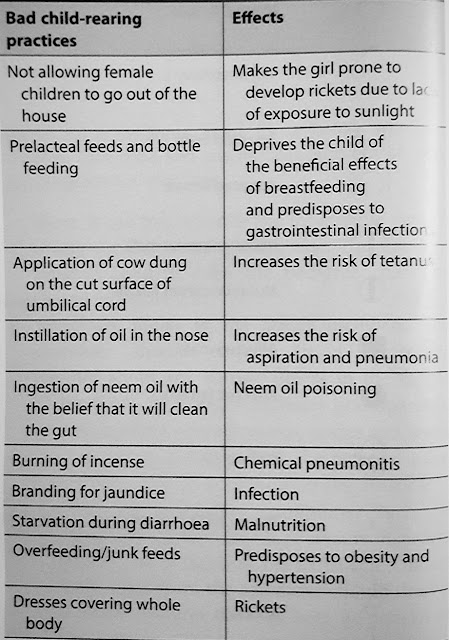 |
| The above picture is taken from Aruchamy Textbook of Paediatrics |
*******
Topic 4 - DIET HISTORY: (04)
Calorie Deficit percentage:
<20% - Normal growth
10-20% - Undernutrition
20-30% - MAM
30-40% - SAM
Protein requirement in child - simple formulae
Expected weight x 2 g/kg
(Expected weight is taken from 50th percentile of Harvard standard from growth charts)
(Expected weight is taken from 50th percentile of Harvard standard from growth charts)
How MILK diet history is asked?
Milk is usually diluted with water
So, you should ask amount of milk itself used (not the amount of milk consumed by the child, as it contains water also)
So, you should ask amount of milk itself used (not the amount of milk consumed by the child, as it contains water also)
Rule of thumb to remember calorie requirement
Upto 1 year - 1000 kcal
After that, for every year: add 100 kcal
This will give calorie req in approx for that age (for ex: 2 yrs - 1100 kcal and 8 yrs - 1700 kcal)
Upto 1 year - 1000 kcal
After that, for every year: add 100 kcal
This will give calorie req in approx for that age (for ex: 2 yrs - 1100 kcal and 8 yrs - 1700 kcal)
